OFFSET FETCH语句
语法
The following illustrates the syntax of the OFFSET and FETCH clauses:
ORDER BY column_list [ASC |DESC]
OFFSET offset_row_count {ROW | ROWS}
FETCH {FIRST | NEXT} fetch_row_count {ROW | ROWS} ONLY
In this syntax:
- The
OFFSETclause specifies the number of rows to skip before starting to return rows from the query. Theoffset_row_countcan be a constant, variable, or parameter that is greater or equal to zero. - The
FETCHclause specifies the number of rows to return after theOFFSETclause has been processed. Theoffset_row_countcan a constant, variable or scalar that is greater or equal to one. - The
OFFSETclause is mandatory while theFETCHclause is optional. Also, theFIRSTandNEXTare synonyms(同义词) respectively so you can use them interchangeably(可互换). Similarly, you can use theFIRSTandNEXTinterchangeably.
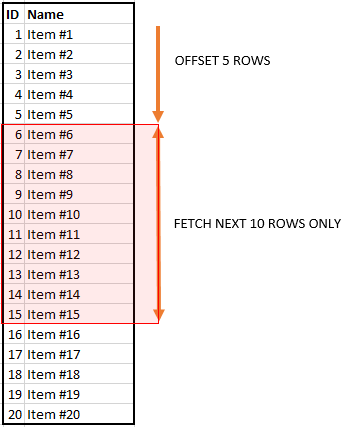
The following illustrates the OFFSET and FETCH clauses:
Note that you must use the OFFSET and FETCH clauses with the ORDER BY clause. Otherwise, you will get an error.
We will use the products table from the sample database for the demonstration.
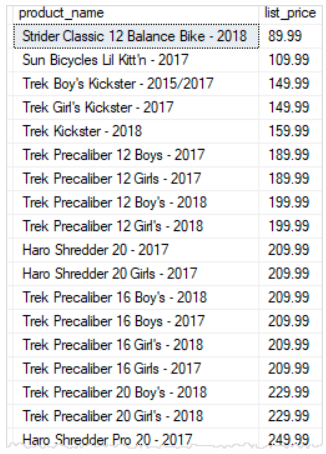
The following query returns all products from the products table and sorts the products by their list prices and names:
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
production.products
ORDER BY
list_price,
product_name;
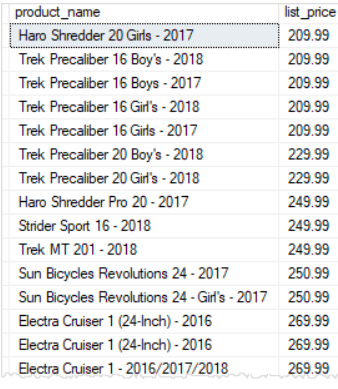
To skip the first 10 products and return the rest, you use the OFFSET clause as shown in the following statement:
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
production.products
ORDER BY
list_price,
product_name
OFFSET 10 ROWS;
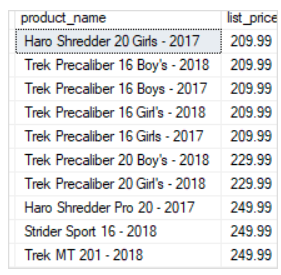
To skip the first 10 products and select the next 10 products, you use both OFFSET and FETCH clauses as follows:
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
production.products
ORDER BY
list_price,
product_name
OFFSET 10 ROWS
FETCH NEXT 10 ROWS ONLY;
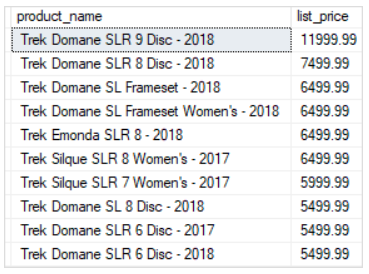
To get the top 10 most expensive products you use both OFFSET and FETCH clauses:
SELECT
product_name,
list_price
FROM
production.products
ORDER BY
list_price DESC,
product_name
OFFSET 0 ROWS
FETCH FIRST 10 ROWS ONLY;
In this example, the ORDER BY clause sorts the products by their list prices in descending order. Then, the OFFSET clause skips zero row and the FETCH clause fetches the first 10 products from the list.
分页实现:Offset-Fetch
Offset-Fetch子句要求结果集是有序的,因此,只能用于order by 子句中,语法如下:
ORDER BY order_by_expression [ ASC | DESC ] [ ,...n ] [ <offset_fetch> ]
<offset_fetch> ::=
{
OFFSET { integer_constant | offset_row_count_expression } ROWS
[ FETCH NEXT {integer_constant | fetch_row_count_expression } ROWS ONLY ]
}
关键字解析:
- Offset子句:用于指定跳过(Skip)的数据行;
- Fetch子句:该子句在Offset子句之后执行,表示在跳过(Sikp)指定数量的数据行之后,返回一定数据量的数据行;
- 执行顺序:Offset子句必须在Order By 子句之后执行,Fetch子句必须在Offset子句之后执行;
分页实现的思路:
- 在分页实现中,使用Order By子句,按照指定的columns对结果集进行排序;
- 使用Offset子句跳过前N页:Offset (@PageIndex-1)*@RowsPerPage rows;
- 使用Fetch子句呈现当前Page:Fetch next @RowsPerPage rows only;
使用order-offset-fetch分页
创建示例数据
use tempdb
go
create table dbo.dt_test
(
id int,
code int
)
go
insert into dbo.dt_test(id,code)
values(1,1),(2,2),(3,1),(4,2),(5,1),(6,2)
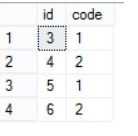
使用Offset子句跳过指定数目的数据行
select *
from dbo.dt_test
order by id
offset 2 rows
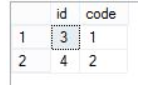
使用Offset-Fetch子句跳过指定数目的数据行之后,返回指定数目的数据行
select *
from dbo.dt_test
order by id
offset 2 rows
fetch next 2 rows only
修改成分页的通用格式
--分页的索引,页码从1开始
declare @PageIndex int
--每页显示的行数
declare @Size int
set @PageIndex=1
set @Size=100
select *
from dbo.dt_test
order by id
offset (@PageIndex - 1) * @Size rows
fetch next @Size rows only
排序(order by)
order by子句的语法是:ORDER BY order_by_expression ,用于按照指定字段进行排序,通常有3种写法:
- select子句中列的name,或alias,排序子句(order by)的执行顺序在select子句之后,可以使用列的Alias进行排序;
- 表达式,按照表达式的计算结果进行排序;
- select子句中列的序号,从1开始,此处的数值是序号,不建议使用;
上述三种写法都会对查询结果集进行排序,返回的结果集是有序的,但是,如果这样写,在order by子句中使用一个常量:
order by (select 1)
该子句中的 1 不是列的序号,而是常量,SQL Server按照结果集的原始顺序返回,order by子句不对结果集排序。
参考